Intestinal lymphangiectasia is a rare condition where tiny vessels in the intestine, called lymphatic vessels, become enlarged and leak a fluid called lymph into the gut. This can cause the body to lose important proteins, leading to low protein levels in the blood and swelling in the legs, feet, or face.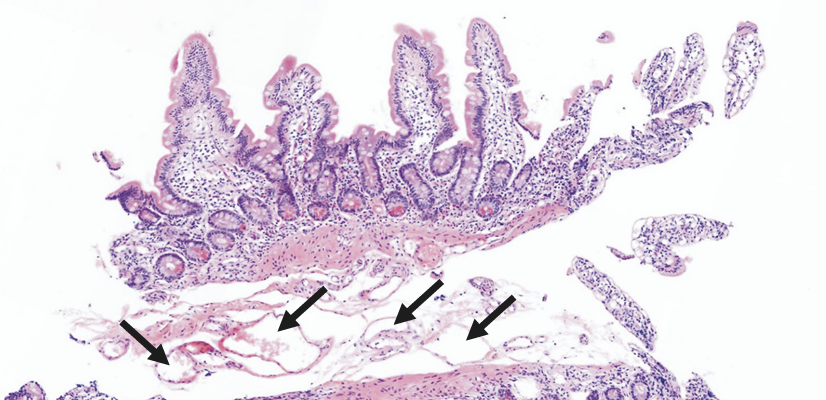
Types of Intestinal lymphangiectasia
Intestinal lymphangiectasia is classified
into primary or secondary types. Primary intestinal lymphangiectasia, also called idiopathic
lymphangiectasia, occurs congenitally in the absence of causative factors. Secondary
intestinal lymphangiectasia is induced by risk factors including heart surgery, chemotherapy,
infection, or toxic materials known to trigger lymphatic changes
Symptoms of Intestinal lymphangiectasia
The most prominent clinical symptom is generalized edema accompanied by chronic diarrhea.