Proton therapy for brain tumor
We would like to introduce the details of proton therapy for brain tumor.
- 01.
- In which cases of brain tumor and spinal tumor can proton treatment be applied?
-
It can be applied when performing an operation is difficult, complete removal has not been achieved, or radiotherapy is needed after the operation. Furthermore, it is especially preferred when treating a pediatric tumor.
- [FAQ] What is a brain tumor?
-
- The most significant characteristic that differentiates a brain tumor from other tumors is that a brain develops in the cranium. In the cranium, there isn’t enough room for other tissues to expand. Therefore, if the brain pressure increases as the tumor grows bigger, symptoms including headaches and vomiting may appear. If a particular part of the brain becomes weighed down by the pressure, it can cause disorders in a certain function of the brain. It is uncommon for a brain tumor to be transferred to other organs. Men and women are exposed to a similar level of risk for most tumors, however, tumors such as meningioma develops more frequently in women and medulloblastoma appears more frequently in men.
- [FAQ] What are the symptoms associated with the positioning of a brain tumor?
-
- Our brain is composed is a similar way to our stomach and when tumors develop in each region, the following symptoms may appear.
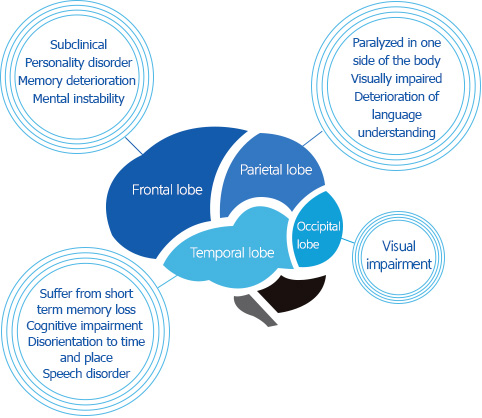
- Frontal lobe - Subclinical, Personality disorder, Memory deterioration, Mental instability
- Parietal lobe - Paralyzed in one side of the body, Visually impaired, Deterioration of language understanding
- Temporal lobe - Suffer from short term memory loss, Cognitive impairment, Disorientation to time and place, Speech disorder
- Occipital lobe - Visual impairment
[Symptoms According to the Position of the Brain Tumor]
- 02.
- What are the advantages of treating brain tumors and spinal cord tumors with proton treatment?
-
Proton treatment minimizes side effects in important organs including the brain, facial area (including eyes and ears), and the spinal cord to decrease the chance of recurrence.
Brain, brain fundus, and spinal cord tumors from close to the organs that are needed for survival (facial structure including eyes and ears and nervous system including brain, cerebellum, and spinal cord). Therefore, precise surgical operation is difficult to implement. Due to the concerns for the development of side effects, a sufficient level of radiation cannot be transferred and therefore, recurrent cancer commonly occurs. Especially in the case of the X-ray treatments, side effects such as necrosis appears near the brain and radiation is exposed to distant normal brain tissues especially near the hippocampus decreasing brain cognitive functions. This generates problems in the patient’s quality of life.
-
Proton treatment has a physical characteristic called, “Bragg Peak,” in that significant decreases in the level of radiation transferred to the normal organs, especially to the normal brain and hippocampus near the tumor, which can reduce the possibility associated to decline in brain cognitive functions.
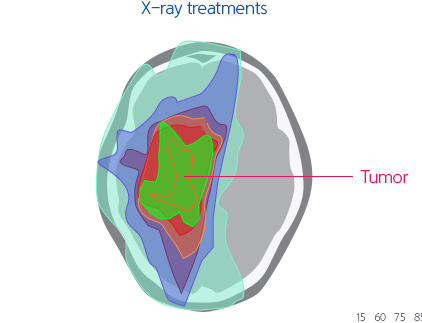
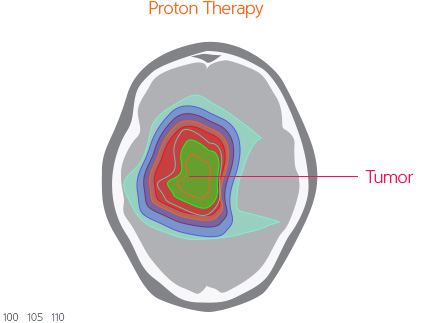 [Proton Therapy compared to the X-ray treatments to treat brain tumor]
[Proton Therapy compared to the X-ray treatments to treat brain tumor] -
Furthermore, radiotherapy is known to help improve the tumor control rate in the cases where complete removal has not been achieved in a spinal tumor operation. Even though the transfer of sufficient radiation can be limited due to the normal spinal cord’s low resistance to radiation, it is expected that proton treatment will not increase the possibility in myelitis development and raise the application of radiation to improve tumor control rate.
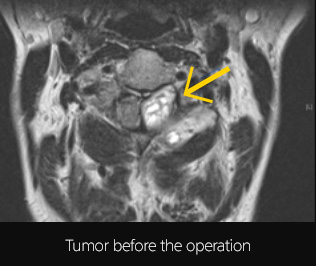
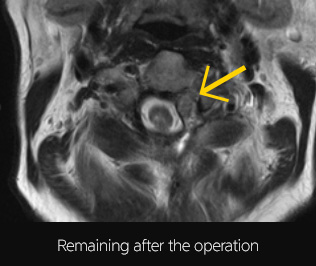 [In the case where complete removal of a spinal cord tumor is difficult with surgical operation]
[In the case where complete removal of a spinal cord tumor is difficult with surgical operation]
- 03.
- What are the effects of the treatment?
-
It is being reported that the tumor control rate can be improved through proton treatment when applied to brain fundus chordomas or chondrosarcoma patients who cannot be treated through surgical operation or patients with some remaining tumor sites after the surgical operation.
Furthermore, increasing the radiation dose in the general radiation or contact radiation therapy for glioblastoma did not draw effective clinical outcomes. However, improved clinical outcomes were reported compared to the existing results with the proton treatment, which increased the radiation dose to the sites with higher risks, without exposing radiation to normal tissues including the brain.
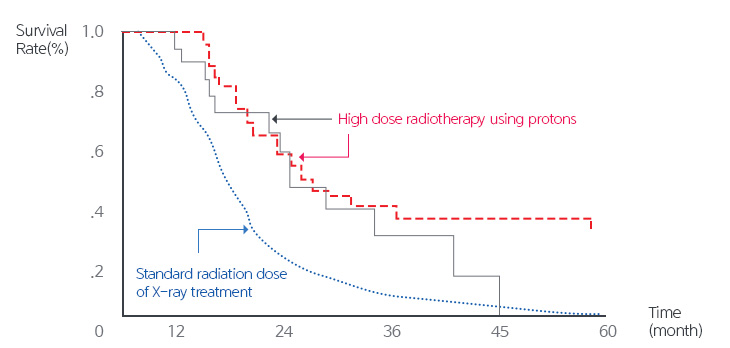
[Survival rate during radiotherapy alone after the operation]
※ However, there are merely no reports on the high dose radiation of the proton treatment with the anticancer drug, “Temodal,” for patients with prolonged overall survival through a combination of radiotherapy and temodal dosing.



