Proton therapy for pancreatiocobiliary cancer
We would like to introduce the details of proton therapy for pancreatiocobiliary cancer.
- 01.
- In which cases of pancreaticobiliary cancer can the proton treatment be applied?
-
If surgical operation is difficult implement on advanced tumors and borderline resectable tumors.
Furthermore, proton treatment can be a good alternative in the case operation of pancreatobiliary cancer is difficult due to the close formation of important near the treatment site.
-
In the case of pancreatobiliary recurrence
Recurrence of cancer is common after the operation of pancreatobiliary cancer. The proton treatment minimizes radiation exposure to the surrounding organs (stomach, duodenum, small intestine, large intestine, liver, kidney) while increasing the level of radiation applied to the tumor, decreasing the risks associated with recurrent cancer.
The effects and necessity of radiotherapy for pancreatobiliary cancer is still a controversial issue. The main cause encompassing the controversy may be the fact that radiotherapy has risk of side effects and it does not transfer sufficient amount of radiation to the cancer site. On the contrary, we expect that the proton treatment may be the answer to the ongoing controversy because minimizes radiation exposure to nearby normal organs, and at the same time, it supplies sufficient level of radiation to the cancer sites.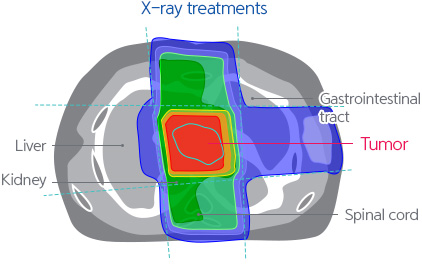
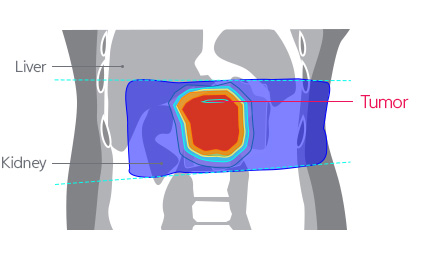
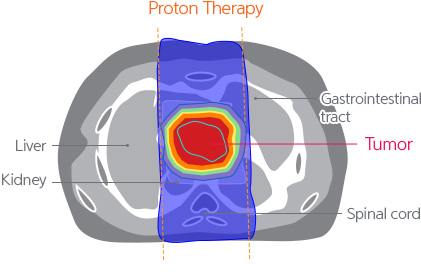
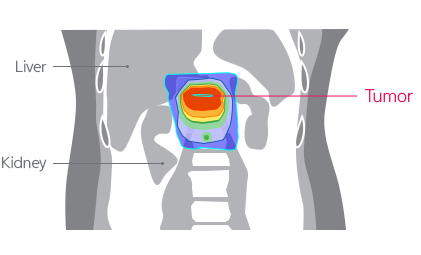 [Proton Therapy compared to the X-ray treatments to treat pancreatiocobiliary cancer]
[Proton Therapy compared to the X-ray treatments to treat pancreatiocobiliary cancer] -
In addition, when treating the patient through chemotherapy together with radiation therapy, the intensity of the chemotherapy is normally adjusted due to the side effects caused by the radiation in comparison to the single chemotherapy. However, with proton treatment, the effect of reducing the remote metastasis through non-adjusted chemotherapy can be drawn, because low probability of side effect occurrence is expected.
* Remote metastasis: Disease transferred to an organ located far apart
- 02.
- What are the effects of the treatment?
- Until now, there has not been a high number of clinical application of proton treatment for the pancreatobiliary cancer. However, there were many analytical studies have been facilitated to assess the proton treatment and the existing radiation treatment’s (3 dimensional conformal radiotherapy, Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy) the level of radiation transferred in the patients. Through the studies, many significant documents have been collected. From these studies, it has been verified in many instances that the proton treatment significantly decreased the radiation exposure to the small intestines, liver, kidneys, and surrounding organs. Moreover, it has been reported in many cases that proton treatment maintained low levels of side effects in the gastrointestinal tract and relatively high tumor control rates with high survival rates.



