
Lim, Do Hoon
Professor & Chairman Department of Radiation Oncology Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Special Interests : 뇌종양, 소아암, 위암, 위말트림프종, 중추신경계림프종, 육종(척추), 다발성골수종, 양성자치료
We would like to introduce the details of proton therapy for stomach cancer.
Proton treatment can be applied to all stomach cancer that needs radiotherapy and in particular, the most effective outcome can be achieved for recurrent stomach cancer.
For recurrent stomach cancer where the surgical operations are hard to be applied
After surgical operation for the concomitant of stomach cancer with metastatic lymph nodes.
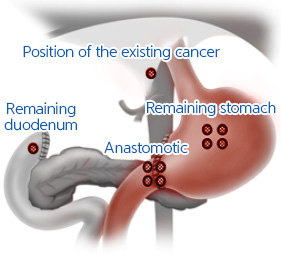
[Topical recurrence]
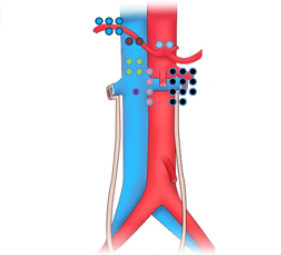
[Lymph node recurrence]
It can reduce the side effects of normal organs and the occurrence of secondary cancer. Moreover, it can improve tumor control rates through high doses of proton treatment for recurrent stomach cancer.
If stomach cancer has recurred where surgical operations are not applicable, some radiotherapies are considered to be implemented as an additional treatment with chemotherapies.
However, transferring a sufficient radiation dose is hard to achieve since normal organs around the abdominal sites (including duodenum, small and large intestine, liver, kidney) are vulnerable to radiation.
In this case, proton treatment can be applied in order to increase the tumor control rate safely.
In the case of stomach cancer, the role regarding radiotherapy is still controversial, however, according to the randomized 3 phase study implemented by our hospital, a tumor was removed and the progression-free survival was increased when the combined treatment of chemotherapy and radiotherapy were applied to the stomach cancer with lymph nodes metastasis after the surgical operation. When applying the combined treatment of chemotherapy and radiotherapy to stomach cancer with lymph nodes metastasis after surgical operation, the radiation dose can be safely increased and chemotherapy can be implemented with a sufficient radiation dose without concerns regarding an acute/subacute side effects.
[Result of the Randomized, 3 Phase Study ]
| Recurrence location | Overall | Lymph node metastasis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radiotherapy Yes (n=228) |
Radiotherapy No (n=230) |
P-value |
Radiotherapy Yes (n=228) |
Radiotherapy No (n=230) |
P-value |
|
| Number of topical recurrence patients (%) | 29(12.7) | 15(6.5) | 0.03 | 28(14.5) | 13(6.4) | 0.009 |
| Number of remote metastasis patients (%) | 55(24.1) | 51(22.2) | 0.66 | 48(24.9) | 45(22.7) | 0.64 |
| Number of recurrence patients (%) | 77(33.8) | 60(26.1) | 0.08 | 69(35.8) | 53(26.1) | 0.04 |
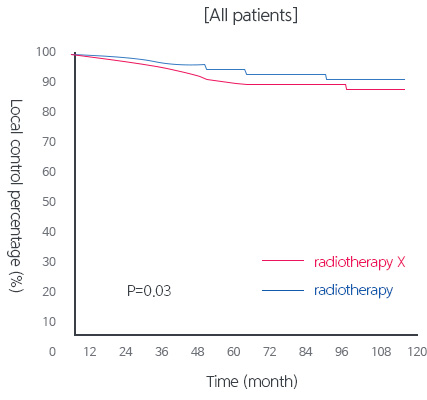
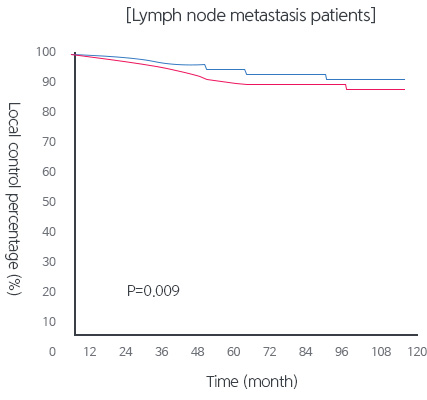
There are few studies that have been conducted on proton treatment applied to stomach cancer. However, according to our hospital that implemented the randomized 3 phase study, the efficacy of removing tumors through radiotherapy was confirmed.
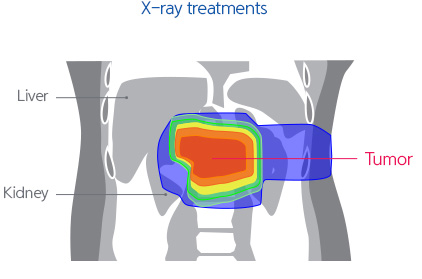
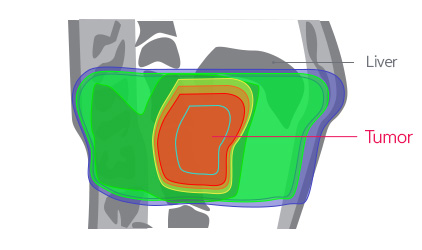
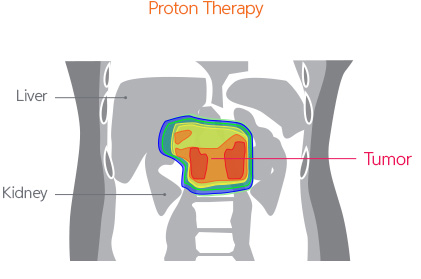
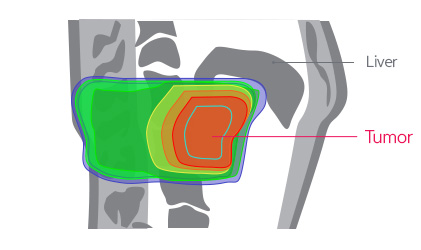
Moreover, according to the study conducted by our hospital to assess the transferred radiation dose by comparing proton treatment to X-ray treatments, it was confirmed that the radiation dose exposed to most of the normal organs was significantly lower in the proton treatment compared to X-ray treatments.
However, the actual clinical approach of the proton treatment is rare and there are not many cases which confirm the efficacy of the proton treatment that can remove tumors without significant side effect by transferring a high radiation does safely through applying this approach to stomach cancers where surgical operations are not applicable.

Professor & Chairman Department of Radiation Oncology Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Special Interests : 뇌종양, 소아암, 위암, 위말트림프종, 중추신경계림프종, 육종(척추), 다발성골수종, 양성자치료

Radiation Oncology "Instructor, Department of Radiation Oncology, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center" Special Interests : 대장/직장/항문암, 간암, 췌장암, 담도암, 위암, 육종(복부/후복부/상/하지), 양성자치료