Why Choose SMC?
Realizing Patient-Centered Care
We are committed to providing medical services that prioritize each patient's unique experience – ensuring personalized, respectful, and collaborative care at every step.
At Samsung Medical Center (SMC), we blend cutting-edge medical technology with compassionate care, ensuring that each patient receives individualized treatment with respect and empathy throughout their journey.
We are committed to providing medical services that prioritize each patient's unique experience – ensuring personalized, respectful, and collaborative care at every step.
International Healthcare Center (IHC) is a center dedicated solely to the care of patients at Samsung Medical Center (SMC), one of South Korea's leading hospitals. IHC opened in September 1995 and is the premier medical clinic for resident expatriates and patients in Korea.
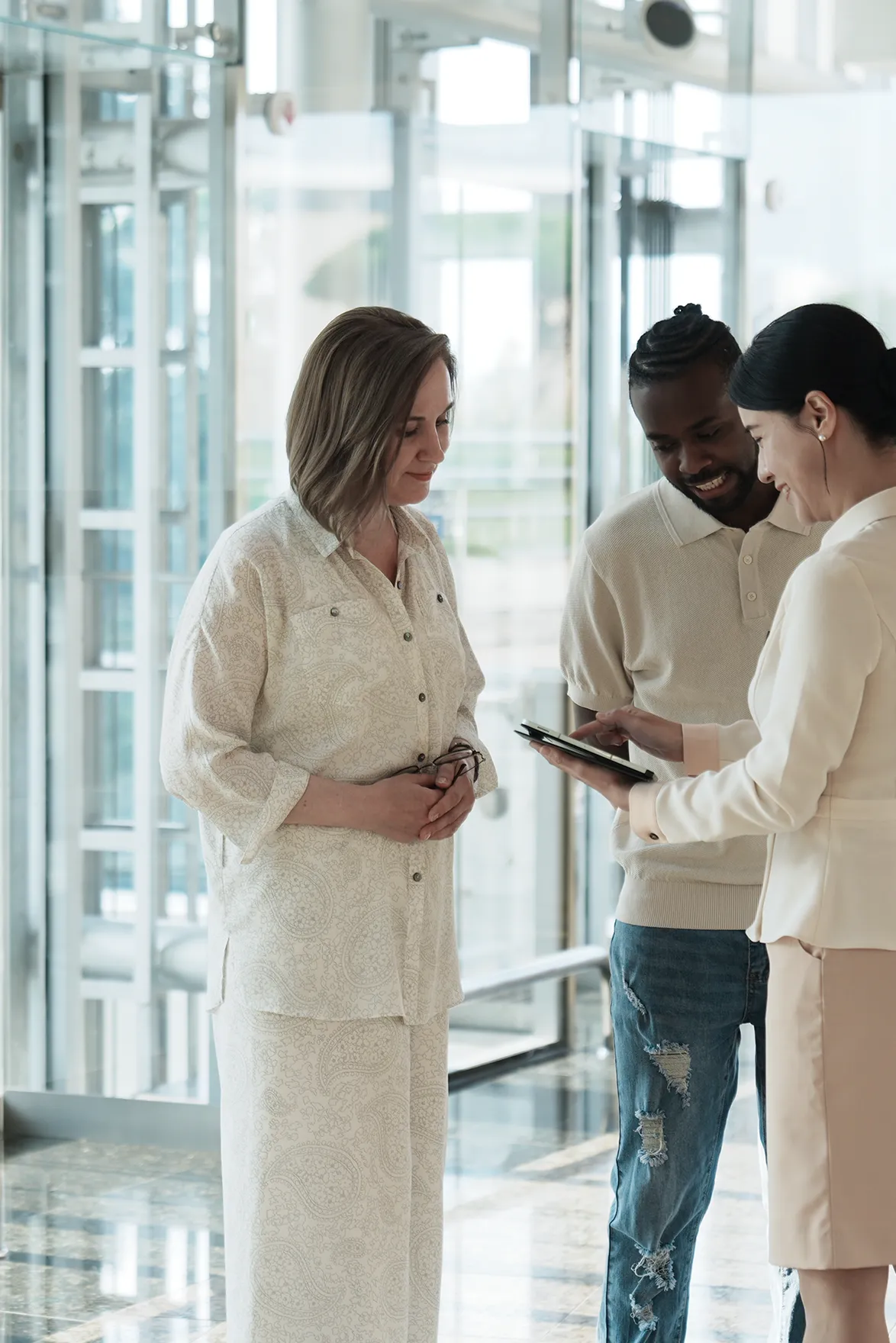

We offer dedicated service tailored to your needs, with specialized staff who bring proven expertise to every detail — delivering exceptional results you can trust.
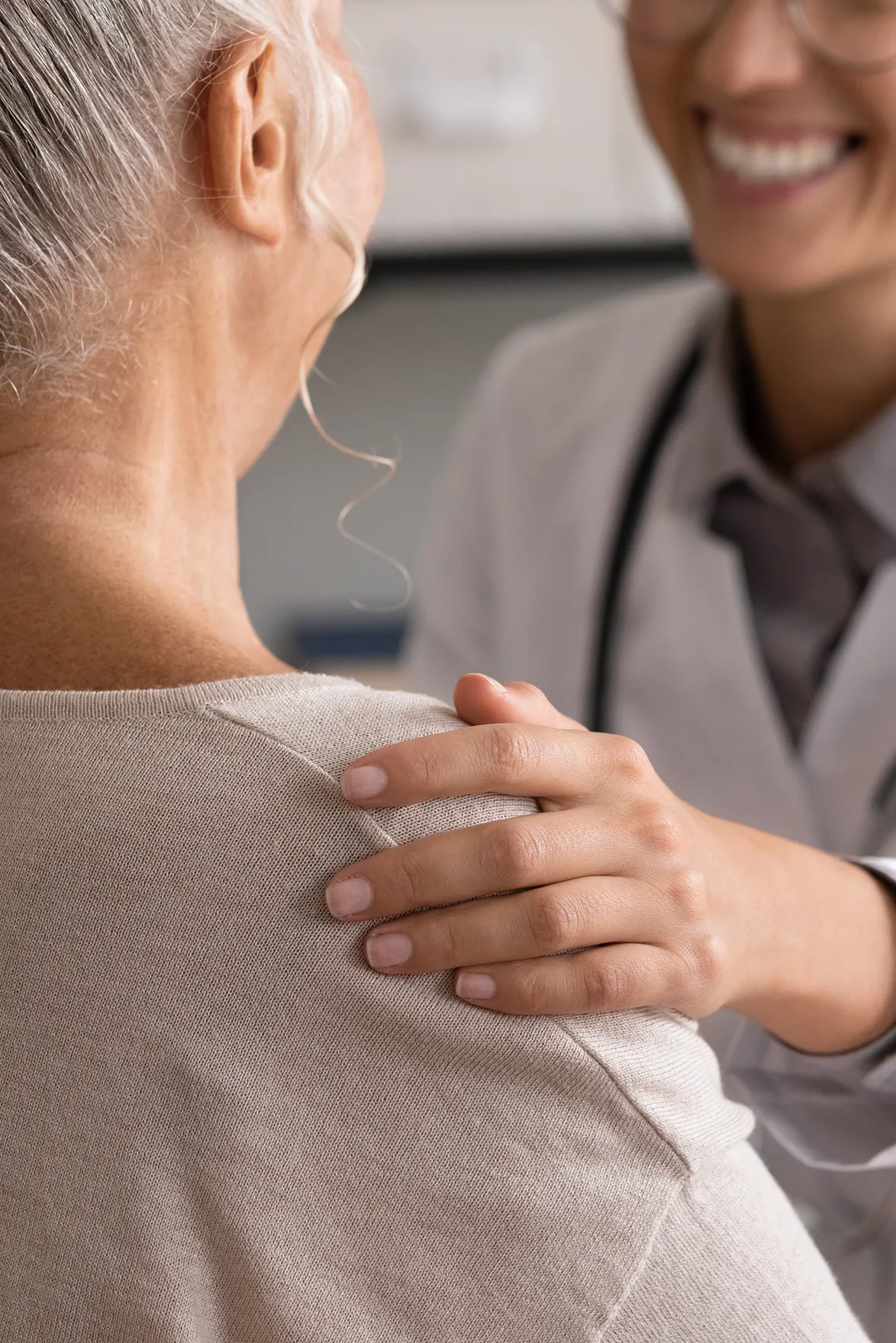

With access to the latest technologies, clinical trials, and personalized medicine, we deliver cancer care that's both scientifically advanced and deeply human.
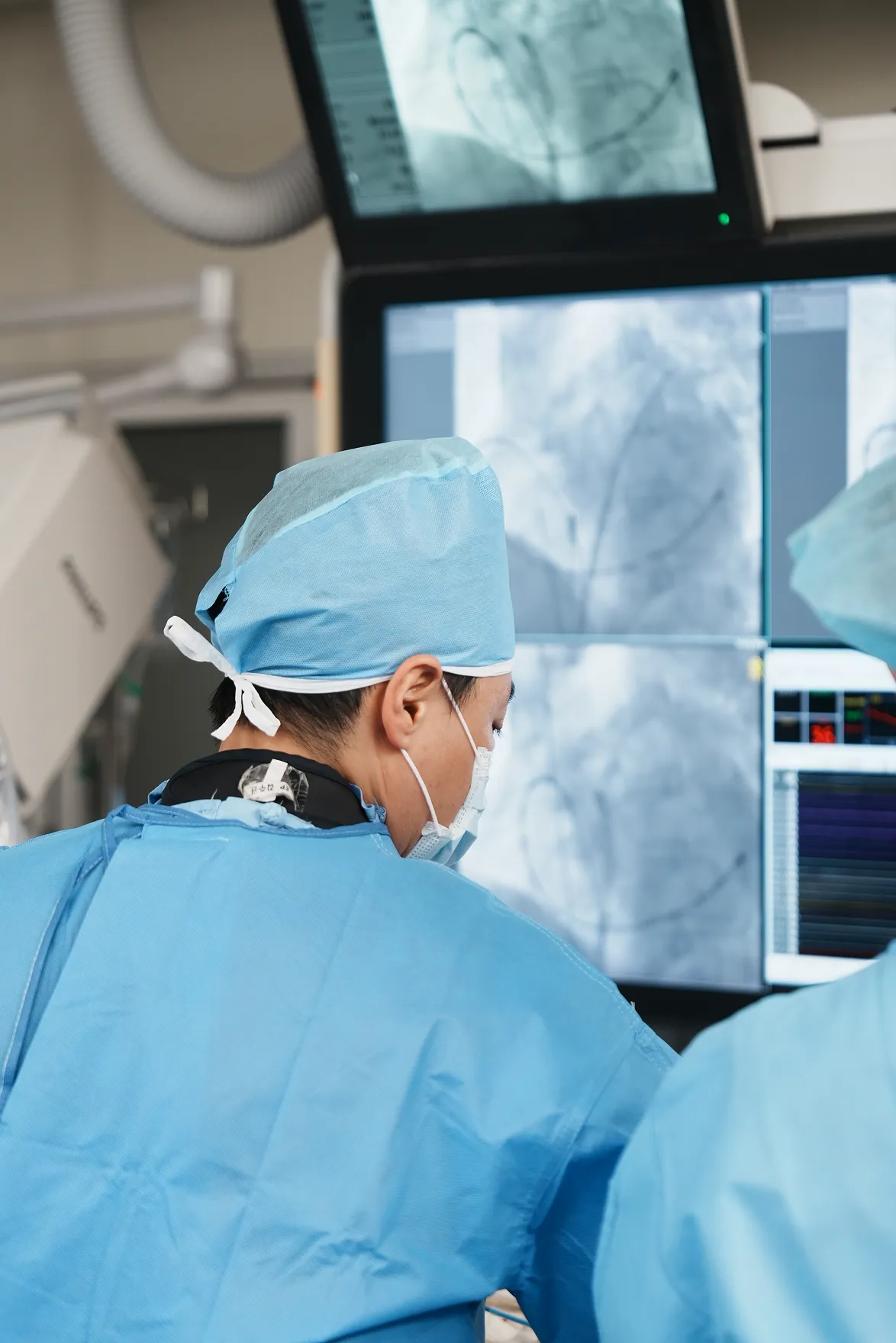
Our center offers comprehensive, patient-focused care for a wide range of cardiovascular and neurological diseases – delivered by a team of leading specialists using the latest in medical innovation.
And that's just the beginning.
We also offer care across more than 50 other specialties led by top experts in every field.
Schedule your journey now